China CNC Milling » Blog » Analysis of engine crankshaft processing technology
FAQ
What materials can you work with in CNC machining?
We work with a wide range of materials including aluminum, stainless steel, brass, copper, titanium, plastics (e.g., POM, ABS, PTFE), and specialty alloys. If you have specific material requirements, our team can advise the best option for your application.
What industries do you serve with your CNC machining services?
Our CNC machining services cater to a variety of industries including aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, robotics, and industrial equipment manufacturing. We also support rapid prototyping and custom low-volume production.
What tolerances can you achieve with CNC machining?
We typically achieve tolerances of ±0.005 mm (±0.0002 inches) depending on the part geometry and material. For tighter tolerances, please provide detailed drawings or consult our engineering team.
What is your typical lead time for CNC machining projects?
Standard lead times range from 3 to 10 business days, depending on part complexity, quantity, and material availability. Expedited production is available upon request.
Can you provide custom CNC prototypes and low-volume production?
Can you provide custom CNC prototypes and low-volume production?
Hot Posts
The crankshaft is one of the most important parts in the engine.
Its structural parameters and processing technology level not only affect the size and weight of the whole machine. They also greatly influence the reliability and lifespan of the engine.
Therefore, it is very important to improve the crankshaft processing method and improve the processing accuracy.
Current status of crankshaft processing technology
Since the 21st century, the engine crankshaft has undergone tremendous changes in manufacturing technology, tools, etc.
Some advanced countries widely use CNC technology and automatic lines in crankshaft machining. Several independent automated production units generally form the production line, giving it high flexibility and adaptability.
The rough processing of the journal generally adopts CNC milling and turning processes, while grinding widely adopts fully CNC and fully enclosed automatic lines.
● Processing technology types
The roughing and semi-finishing processes of crankshaft main journals and connecting rod journals are generally classified into the following types:
1 Traditional multi-tool turning process of crankshaft main journals and connecting rod journals;
2 CNC turning process;
3 CNC internal milling process;
4 CNC turning-drawing process;
5 CNC turning-turning-drawing process;
6 CNC high-speed external milling process;
7 Composite processing technology.
After analysis and comparison, we can see that CNC turning equipment is relatively inexpensive, requires no complex tools, and is suitable for small-batch production.
The price of internal milling equipment is relatively high, the tool cost is very high, and it is suitable for large-scale production;
The outstanding advantages of turning-drawing and turning-turning-drawing are that they can perform layered processing on wide shaft diameters, with high cutting efficiency and good processing quality.
The turning-drawing tool has a complex structure, high technical content, and has long relied on imports. In addition, the turning-turning-drawing process requires two processes to process the connecting rod journal.
CNC high-speed external milling has a wide range of applications, especially double-disc CNC high-speed external milling, which has become the current development direction of rough machining of crankshaft main journals and connecting rod journals due to its high machining efficiency, stable machining quality and high level of automation.
The new CNC high-speed crankshaft external milling machine tools that appeared in the mid-1990s have taken the crankshaft rough machining process to a new level.
● Differences between CNC crankshaft internal milling and CNC high-speed crankshaft external milling
Internal milling has the following disadvantages:
It is not easy to align the tool, the cutting speed is low (usually not more than 160m/min), the non-cutting time is long, the machine tool investment is large, and the process cycle time is long.
CNC high-speed crankshaft external milling has the following advantages:
High cutting speed (up to 350m/min), short cutting time, short process cycle time, small cutting force, low workpiece temperature rise, long tool life, fewer tool changes, higher processing accuracy and better flexibility.
Therefore, CNC high-speed crankshaft external milling will be the development direction of crankshaft rough machining.
Crankshaft machining process using CNC turning-turning-pulling machining
In the late 1980s, Germany developed a perfect crankshaft turning-turning-pulling machine tool, and then other countries’ machine tool companies also produced turning-turning-pulling machine tools in recent years.
This processing technology is a perfect combination of crankshaft turning technology and crankshaft turning and drawing technology. It has high production efficiency, good processing accuracy, strong flexibility, high degree of automation, and short tool change time. It is particularly suitable for the processing of crankshafts with undercut grooves. After processing, the crankshaft can be directly fine-ground, eliminating the rough grinding process.
Therefore, the crankshaft turning-turning and drawing processing technology is one of the popular processing technologies in the rough processing of crankshafts in the world.
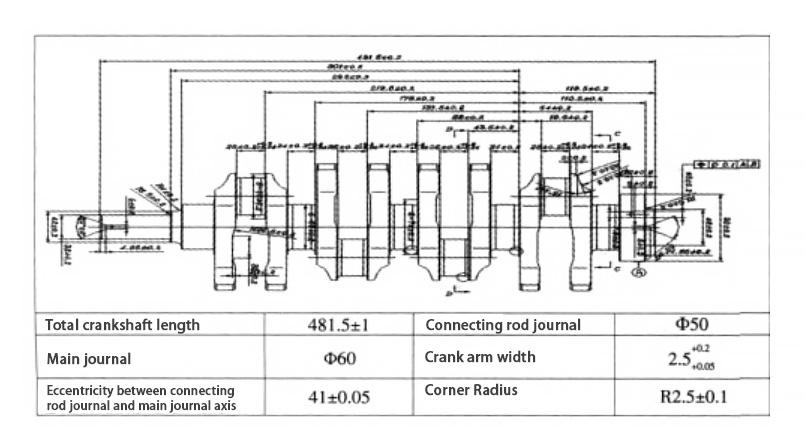
The following is a specific example to illustrate the crankshaft processing technology using the turning-turning and drawing CNC processing method. Table 1 shows the typical crankshaft part drawing along with its main parameters.
Crankshaft processing generally begins with the main journal, followed by the connecting rod journal. The thrust stop acts as the axial positioning reference, while the flange provides lateral positioning.
Processing starts from the blank, with the side machined first.If the workpiece is not a blank, base alignment must be performed before processing.
For finishing, leave 1mm on each side, and for the blank, leave 2~2.5mm on each side. See Table 2 for specific processing procedures.
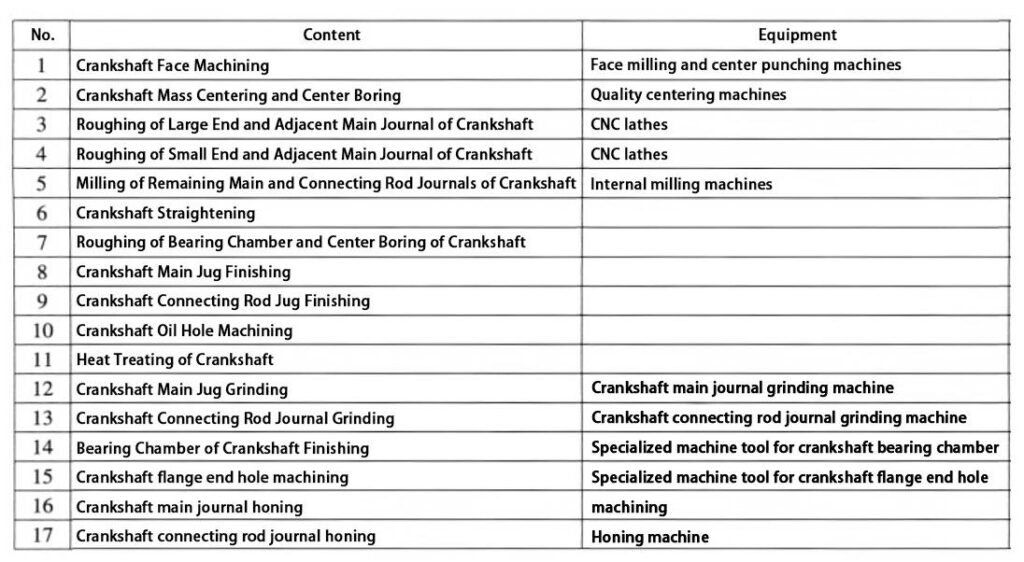
From the above process, it is evident that CNC machining can complete the crankshaft connecting rod journal’s outer surface, shoulder, thrust face, fillet, or undercut groove with high precision and efficiency.
Crankshaft compound machining technology
From the perspective of manufacturing industry development, compound machining machine tools will remain key products for advancement. As technology continues to improve, their functions will expand, moving toward the concept of ‘one machine tool becoming a small factory.
Among the crankshaft compound machining machines, the horizontal turning and milling compound machining center produced in Austria is representative.
It puts forward the concept of “one clamping, all completed”.
The turning and milling center integrates a dual-spindle turning center, a five-axis machining center, deep hole boring, milling, drilling and three-coordinate functions.
The crankshaft can be fully machined on a dual-spindle turning and milling compound machining center, and the processed crankshaft can then be directly transferred to the finishing stage.
In crankshaft finishing, process-integrated CNC grinders with cubic boron nitride tools can grind all main journals and connecting rod journals in a single clamping.
Such grinders are generally equipped with double grinding wheel heads.
It can meet the needs of multi-variety, low-cost, high-precision, and mass production. It applies the workpiece rotation and grinding wheel feed servo linkage control technology.
This method completes the grinding of all journals in one clamping without altering the crankshaft’s rotation center, including follow-up tracking grinding of the connecting rod journals.
It adopts hydrostatic spindle, hydrostatic guide rail, hydrostatic feed screw (grinding wheel head) and linear grating closed-loop control system, and the grinding journal roundness is high and the grinding efficiency is extremely high.
Conclusion
From the above analysis, the following conclusions can be drawn:
The traditional multi-tool turning process of crankshaft main journal and connecting rod journal, ordinary CNC turning process, and ordinary CNC internal milling process will be gradually eliminated over a period of time.
High-speed and efficient CNC turning-pulling process, CNC turning-pulling process and CNC high-speed external milling process have been applied to a considerable extent.
With the continuous improvement of processing technology and equipment and the continuous improvement of cutting tool performance, composite processing technology suitable for multiple varieties and small batches is a development direction for crankshaft processing in the future.